Osteochondrosis is the wear and tear of the intervertebral discs, which leads to degenerative organic changes in the spine. Osteochondrosis of the thoracic spine is considered the rarest, since this section is the least mobile due to its connection with the ribs. However, this is the most insidious and serious and develops earlier than other forms. Treatment of osteochondrosis of the thoracic spine is characterized by an integrated approach and produces good results. With a competent therapeutic approach, people can regain mobility, lightness and a pain-free life.
causes
The main factors causing the development of osteochondrosis of the thoracic spine include:
- Kyphosis and scoliosis. These diseases often accompany a person from birth as an anatomical anomaly. If the kyphosis is smoothed out, a person may not know about its existence for half of his life. Scoliosis is a curvature of the spine that leads to impaired distribution of muscle load. This leads, on the one hand, to atrophy and relaxation of the muscles, and on the other hand, to cramping due to constant tension.
- Injuries. They may be evident when a person injures their vertebrae in a fall, accident, or similar circumstances. The injuries may not be noticeable. For example, spinal injuries often occur due to overuse in the gym and heavy lifting.
- Flat feet. Some doctors argue that this is almost the main reason for the development of degenerative changes in any part of the spine. Flat feet disrupt the balance of the muscular corset, incorrect redistribution of the load leads to impaired devaluation of the vertebrae.
- Statically incorrect posture over a long period of time. Muscle overload causes blood circulation and nutrition of muscle tissue to deteriorate. They hold the spine. This is the cause of osteochondrosis not only of the thoracic spine, but also of the cervical and lumbar spine.
- Obesity and lack of physical activity.
- Stress. Stress itself is not as dangerous as the reaction to it. When stressed, the adrenal glands produce excessive amounts of adrenaline, which is converted into norepinephrine. It promotes the thickening of blood vessel walls and the progression of atherosclerosis. Under stressful conditions, blood vessels constrict, resulting in poor oxygenation of muscle tissue.
- Drinking alcohol, smoking, taking other drugs and poor diet. Alcohol dissolves calcium from bone tissue. Tobacco and other drugs cause blood vessel dysfunction. Serious nutritional errors lead to obesity and deficiencies in B vitamins and minerals.
- Improper carrying of bags and shoes.
- Gastrointestinal diseases that affect the quality of nutrient absorption.
- Violation of water and electrolyte balance over a long period of time.
- Pregnancy. Thoracic osteochondrosis often occurs in women who are pregnant with twins or triplets.
- Metabolic syndrome.
- Autoimmune diseases, infections, poisoning.
- Genetic predisposition associated with a genetic mutation. You should not think that a genetic predisposition is necessarily related to the fact that one of your close relatives suffered from osteochondrosis. Often this has nothing to do with genetics. A genetic predisposition is always a mutation of certain genes. But even so, the disease only develops in combination with other factors.
The disease can occur both in adulthood and in adolescence. Every year the disease becomes younger. Therefore, it is important to detect the problem as early as possible by paying attention to the symptoms.
Symptoms
Degenerative changes in the thoracic spine cause great concern to people. The chest area contains the heart, lungs, internal organs of the abdominal cavity, ribs and, in women, the mammary glands. Symptoms at this point may resemble an angina attack, a heart attack, or pain in the stomach, mammary glands, or other nearby organ. Therefore, when osteochondrosis makes itself felt, it is often confused with other dangerous pathologies.
Symptoms and treatment of osteochondrosis of the thoracic spine are related to two clinical pictures.
Radicular signs
Radicular symptoms:
- stabbing or aching pain in the shoulder, armpits, or collarbone;
- impaired reflexes;
- muscle weakness;
- Pain in the upper chest, similar to a heart attack, in the solar plexus, hypochondrium, pain in the mammary glands, upper abdomen or groin.
Reflex signs
Symptoms:
- Respiratory diseases such as a feeling of lack of air, pain when inhaling and exhaling, difficulty breathing;
- Feeling of chills, "goosebumps";
- Feeling of disturbances in the gastrointestinal tract: nausea, loss of appetite, heartburn, diarrhea or constipation, flatulence;
- intercostal neuralgia;
- Pain in the chest of a belt-like nature, between the shoulder blades, when bending and stretching;
- Insomnia, feeling tired when getting enough sleep, tiredness;
- Stiffness of movement in the morning;
- worsening gait;
- Irritability;
- decreased libido/potency.
Reflex symptoms are less clear than radicular symptoms and are often misunderstood by physicians. Therefore, it is very important to find a competent doctor who will take the patient's complaints seriously and prescribe the correct treatment for thoracic osteochondrosis, especially during an exacerbation.
diagnosis
The gold standard for diagnosing thoracic osteochondrosis is an MRI of the thoracic spine and an examination by a neurologist.
MRI accurately shows the anatomical structure, changes, compression, blood flow and a visual picture of the effect on the spinal cord. The study also shows possible complications of the disease such as bulges, osteophytes, hernias and their effects on blood circulation.
An examination by a competent doctor still plays an important role in making a diagnosis.
Treatment
Many have heard that it is impossible to completely get rid of osteochondrosis, but you can only slow down its development. That's a half-truth. They can eliminate hernias, osteophytes and other complications of the disease. You can regain your life without pain, freedom of movement and restore your intervertebral discs. There is a great chance to stop the destruction process and return the spine to its previous state as much as possible. Some people managed to completely get rid of the pathology, others did not. Everything is individual and depends on the state of health, willingness to overcome difficulties and patience.
You must expect that the treatment of osteochondrosis of the thoracic spine will take a long time. On average, active participation takes 1-3 months. But even then, life will not be the same as regular and adequate physical activity is required for at least a year.
In this case, finances and time are not a reason to refuse treatment, since you can fight the disease both in the hospital or sanatorium and at home. The most convenient option is a sanatorium. There the patient is supported by a group of people with the same problems, but the conditions are positive and homely. The medical staff is always tactful and caring. There you can relax and receive treatment without a hospital atmosphere, but with all the necessary medical services.
Therapy consists of several phases:
- getting rid of pain (wearing a special corset, taking painkillers, undergoing procedures);
- Restoration of damaged intervertebral discs and preventive measures against the progression of the disease (physiotherapy, gymnastics, proper nutrition, help from a psychologist).
Drug treatment is also used, but is considered a last resort if other methods do not help. In the most severe cases and with dangerous hernias, surgery is prescribed.
The most important rule is no self-medication or self-diagnosis. Mistakes can be very costly.
Treatment at home
If you do not have time or enough financial resources for treatment in a clinic or sanatorium, you can achieve impressive results in eliminating osteochondrosis at home. The following recommendations will help you cope with the disease.
Nutrition
It is necessary to include foods in the diet that accelerate metabolism in excess weight and the regeneration of cartilage tissue. It is important that the food you eat is rich in nutrients, microelements, antioxidants, polyunsaturated fatty acids and vitamins and is easy to digest.
You need to eat 4-5 times a day every 2. 5-3 hours, preferably at the same time. Portions should not be more than 300 g so as not to overload the stomach and liver. Three meals should contain 26-30g of protein. Protein is essential for building muscle tissue. As a result, metabolism speeds up, the body stops accumulating fat, and cells receive a constant supply of nutrients.
The first breakfast and dinner should consist predominantly of proteins. For example, egg whites and cucumber. The main principle of the first and last meals is the absence of insulin spikes, which is achieved by eliminating carbohydrates. Although cucumber is a carbohydrate, it has a low glycemic index. Protein without a small amount of fat and carbohydrates is not digestible.
Suggested products:
- Legumes as a protein substitute for meat (beans, including green beans, lentils, peas);
- Vegetables in large quantities (except starchy vegetables, which should be consumed with caution);
- Jelly and jelly (contain natural collagen, necessary for joints);
- chicken wings (the bones must be gnawed, their contents are the most valuable);
- poultry, red meat in limited quantities;
- salmon fish, caviar and milk;
- Squid, seaweed (no more than 100 g at a time);
- Olive oil, camelina oil, linseed oil (if there are no liver problems), sesame oil; Adults should avoid sunflower oil;
- Fruits in limited quantities with low sugar content
It is advisable to cook, steam, braise or eat all dishes fresh.
The drinking regime is mandatory because the required amount of water relieves dehydration, nourishes cells and promotes weight loss. Daily water intake is calculated using a simple formula: 30 x weight. Tea, coffee, herbal teas, juices and fruit drinks are not considered water.
Physical exercises
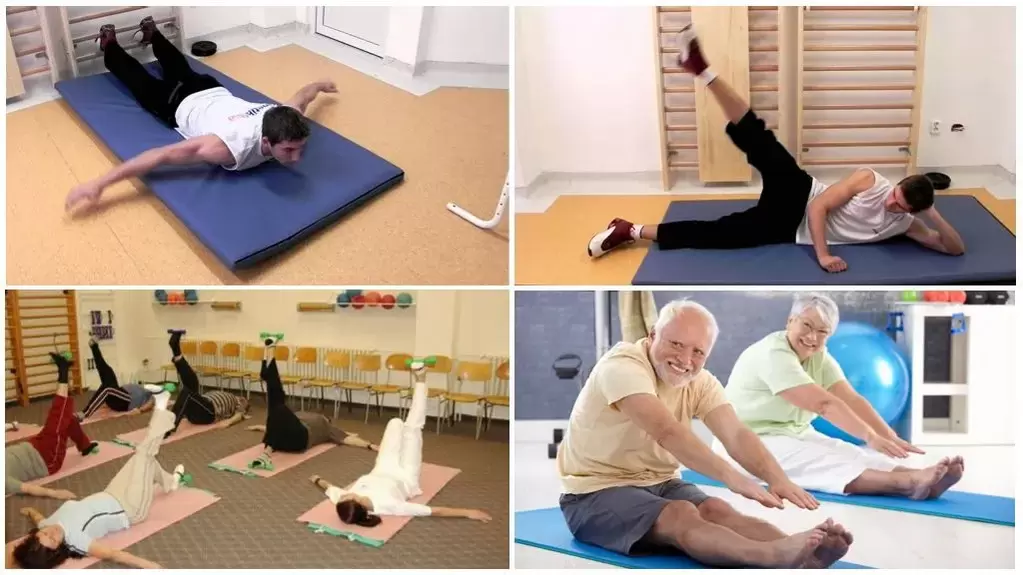

Physical exercise is an essential part of the treatment of osteochondrosis of any part of the spine. The following techniques may be included:
- Gymnastics developed by scientist Yuri Gushcho. It includes elements of dynamic and static yoga. He also advises carrying out hardening procedures. If you're interested, you can read his book "12 Keys to the Longevity Safe" where he talks about what you can do to live as long as possible while being active. It makes sense to trust him becauseYuri independently got out of the wheelchair and recovered from coxarthrosis. He received many awards, thanks to the President of the Russian Federation.
- Gymnastics with the technologies of Dr. Bubnovsky. His technique is very effective and can be done at home. A number of exercises can be found in video format on the Internet, and books with detailed instructions are also available.
- Swimming pool. Swimming not only helps you lose weight, but also strengthens your heart, lungs and develops your back muscles.
- Isometric gymnastics. This type of exercise was originally developed for returning astronauts. Exercises can repair weakened muscles, restore flexibility and range of motion without damaging the joints. Gymnastics is indicated for many diseases of the musculoskeletal system, including osteochondrosis of the thoracic spine.
- Outdoor walks. It is advisable to set aside an hour every day for intensive walks, preferably in parks or along the coast. The aim is to improve cerebral blood flow, muscle nutrition and mood.
- Exercises to correct posture.
Complete calm
It is imperative to develop the habit of going to bed and waking up at the same time. Ideally, you go to bed at 9 p. m. and get up at 5-6 a. m. During this period, the brain manages to restore the functioning of the internal systems of the body and psyche and process all the information that it received the day before. This is particularly important for spinal health.
To sleep, you need to choose the right mattress and pillow. It is better to forget about options that are too soft or too hard.
Treatment in a hospital or sanatorium
Manual therapy
This is an impact on the patient's body with the help of hands to restore metabolism and give the spine the correct shape. The procedure consists of manipulations to restore joint function, a relaxing massage to relieve pain and muscle tension, mobilization to improve blood circulation and relaxation.
The duration of treatment is approximately 3 months.
massage
Both classic therapy and acupressure massage forms are used to treat degenerative changes in the thoracic spine. The massage therapist works with the muscle fibers of the upper back and shoulders to influence the chest area.
Mineral baths
During the procedure, the body's hemodynamics changes. This means that the blood is directed from the center to the periphery and from there to the heart, which drives it through all organs and tissues. This achieves the following effects:
- blood circulation improves;
- the nervous system is strengthened;
- The respiratory system and kidneys function better;
- the adaptive properties of the body increase;
- reducing inflammation;
- relief from pain;
- removal of toxins;
- skin sensitivity increases.
The chemical composition of water affects the effect of a mineral bath on the body of a patient with osteochondrosis. The water temperature influences muscle relaxation and metabolic processes.
acupuncture
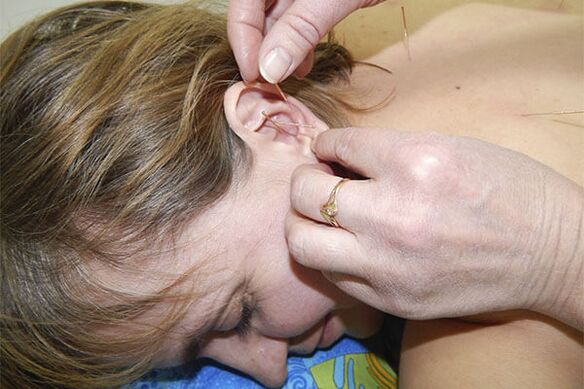
This procedure is also called acupuncture or acupuncture. Its essence lies in influencing biological points of the human body with the help of needles. Long and short sterile needles are inserted to a depth of 15 mm and left for half an hour.
This seemingly simple procedure has proven itself worldwide. Reviews of patients indicate the following effects after completing acupuncture treatment:
- Relaxation;
- cessation of tinnitus and dizziness;
- increasing energy potential;
- improved blood circulation;
- improving thought processes;
- get rid of headaches;
- Relief from muscle spasms.
Laser therapy
The advantage of laser therapy is to improve drug penetration and normalize the body's adaptive properties. During the procedure, laser beams with a specific range are directed at the areas of the spine to be treated. The result of exposure is an anti-inflammatory effect, normalization of metabolism in the affected area, improvement in general well-being, the process of tissue regeneration begins and the degeneration process stops.
By carrying out a complete procedure as part of complex therapy, the degenerative process can be completely reversed.
Mud therapy
This procedure is beneficial not only for the spine but for the entire body. The only thing is that it cannot be used in the acute phase of osteochondrosis.
The effects of mud therapy include improving the trophism of the formations in the intervertebral joints, vascular function, and adaptation and recovery processes. In addition, the functioning of the nervous system is normalized, pain disappears.
Working with a psychologist
Since a person is exposed to constant stress with osteochondrosis, anxiety often develops. A psychologist not only helps to get rid of them, but also stimulates in moments of despair and fatigue. A positive attitude plays an important role in treatment.
Movement therapy
The treatment process is carried out in groups of several people and includes exercises that take into account the individual characteristics of the patient and his medical history. The focus is on improving joint function and strengthening the muscle corset. Without exercise, full recovery is unlikely.
Nordic walking
This is one of the most effective types of physical activity for osteochondrosis and is becoming more and more popular every year.
When walking with sticks, 90% of the muscles are toned, active calorie burning occurs, the load is evenly distributed throughout the body, the cardiovascular system is strengthened, intestinal function is improved, the nervous system and psyche are strengthened, functionsfrom The respiratory system improves, insomnia disappears, blood vessels are strengthened and a strong corset is formed around the thoracic spine.
Drug therapy
Drug therapy is used only in the acute phase of osteochondrosis and when other treatment methods are ineffective.
At the peak of the disease, painkillers are prescribed, as well as drugs that accelerate metabolic processes. Both medication in the form of tablets and injections help.
Prescribed drug groups:
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs that also relieve pain. Available in the form of creams, tablets and ampoules for intravenous or subcutaneous administration.
- Vasodilators. Muscle tension and severe pain cause blood vessels to narrow, which can increase blood pressure and make it more difficult for the brain to receive oxygen. Vasodilators return vascular tone to normal.
- Muscle relaxants. This group of medicines is used to relax and relieve tense muscles. This effect triggers a number of positive changes, such as: B. improved blood circulation, regulation of vascular tone and pain relief. When blood flow normalizes, damaged tissues are restored more quickly.
- Chondroprotectors and B vitamins. These are drugs that restore cartilage tissue and stop the destruction process.
- Complex of sedatives. The stress of the pain makes the pain worse. Irritability and anxiety stimulate the sympathetic nervous system, which leads to even greater tone in the muscles and blood vessels. Sedatives and sometimes antidepressants can break this vicious circle.
As you can see, the treatment of osteochondrosis must be approached comprehensively, studying all the nuances. It is best to contact specialists and protect yourself from mistakes.





















